OCD Definition
This article will explore in-depth the OCD definition, various types of OCD, its causes, symptoms, and examples of OCD, what OCD behavior is, OCD test available, and the treatment of the disorder.
Before moving forward, let us get familiar with the acronym OCD as many of us may not be. The abbreviation OCD is short for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder.
The following content will be worth the read as it provides simple explanations and pointers to gain further insight into the anxiety disorder. OCD has become part of the modern English jargon as it gets used by non-OCD sufferers in talks where they would be referring to someone who is too tidy, overly organized, or very particular about certain things. This misunderstanding of what OCD is stigmatizes those who actually suffer from the disorder. It is completely normal to be a neat freak, to double-check something, to enjoy organizing your closet, have an occasional violent thought, worry that you will get contaminated with germs, but the difference is that for OCD sufferers this will be overwhelming and greatly interfere with their everyday life.
To begin with, Obsessive Compulsive Disorder it is a type of anxiety disorder in which individuals experience persistent and recurrent thoughts, impulses, or images that are involuntary (obsessions) and action repetitive and ritualistic behaviors that are extreme, unnecessary and distressing (compulsions).
Three Main Elements of OCD
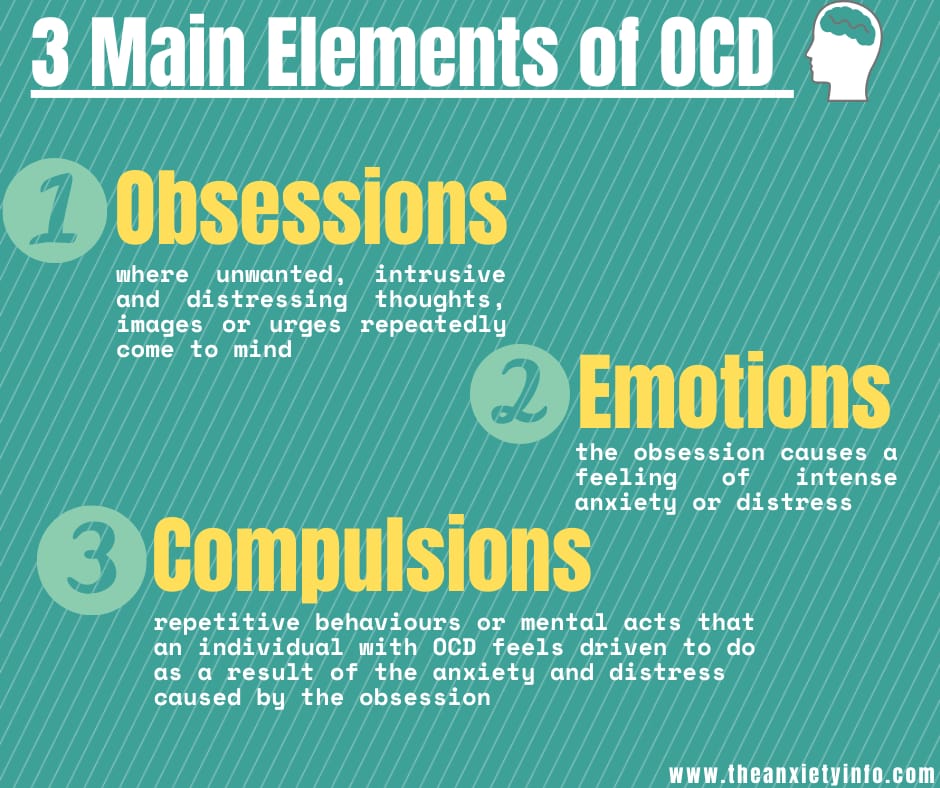
Explained in detail are the 2 main elements; obsessions and compulsive behaviour:
Obsessions
Obsessions refer to recurring, uncontrollable, and unwanted thoughts, sensations, ideas, or feelings. Practically, everyone has unwanted thoughts at some point and it could be things like “have I forgotten to turn off the stove or the iron?” or an unwanted violent image. But the difference is if the thought is persistent and dominates your thoughts to the extent that it interrupts other normal thoughts and take up a lot of your time. It is important to identify if it is an obsession or just a normal thought.
Compulsive behaviour
Compulsions are behaviors that an individual feels the urge to keep repeating over and over again. Compulsions typically start as a technique of trying to prevent or lessen anxiety caused by the obsessive thought. Common forms of compulsive behavior in individuals with OCD include:
- Checking – such as checking if the doors are locked or that the iron is off
- Counting
- Cleaning and hand washing
- Repeating words in their head
- Hoarding
- Ordering and arranging
- Asking for reassurance
- Avoiding circumstances or places which might trigger those obsessive thoughts
It is possible to only have obsessive thoughts or only compulsions, but most individuals with OCD experience both.
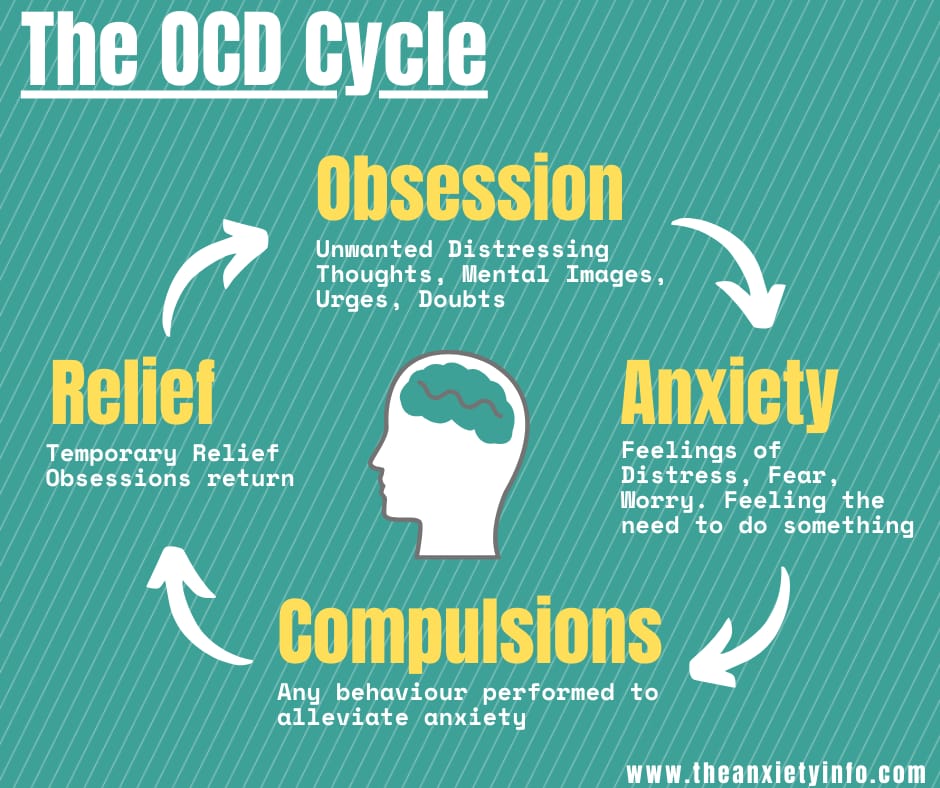
The OCD Cycle
Unfortunately, these obsessive thoughts can be quite distracting and disturbing. In most instances the compulsive behavior momentarily relieves the obsessions and anxiety, for example, if you are terrified of germs then you may get into the habit of cleaning vigorously all the time. However, as this only provides short-term relief, the obsessive thoughts and anxiety typically return much stronger causing the cycle to begin again. Not being able to carry out the obsessive rituals can initiate anxiety and anguish.
Causes of OCD
Even though there has been a considerable amount of research done, experts have not been able to identify a definite cause as to why an individual may develop Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD).
However, there are numerous theories for the possible causes of OCD, including genetics, hormonal changes, environmental factors, biological factors, personality traits, pregnancy, or specific events that can trigger the disorder in an individual. It is highly likely that these factors work together to trigger the development of OCD. Three of the risk factors are further explained below:

Whilst the cause is presently still being debated, what is not in disagreement is the point that OCD is indeed a long-lasting disorder, but equally a treatable medical condition.
It’s also imperative that we don’t become fixated on what causes our OCD at the expense of overcoming it. Recognizing the cause won’t essentially help us overcome it, so our emphasis must continue to be on tackling the problem we have right now.
Symptoms of OCD
Below are a few OCD symptoms to lookout out for if you suspect you or someone you know may have OCD.

Typical obsessive thoughts include:
- Fear of being infected by germs or spreading it to others
- Fear of harming yourself or others by mistake. For example, fear you may set the house on fire by leaving an appliance on
- Fear of self-harming or to others intentionally. For example, fear you may attack someone
- Intrusive sexually explicit thoughts and images
- Excessive apprehensions about illness, morality or religious issues
- Excessive apprehension with orderliness, symmetry, and exactness. For example, you may feel the need to keep making sure all the labels on the tins in your cupboard face the same way.
- Superstitions; extreme attention to something considered lucky or unlucky
Typical compulsive behaviours include:
- Spending an extended amount of time on cleaning and washing
- Extreme double-checking, such as appliances, locks, and switches
- Continually checking in on loved ones to make sure they’re safe
- Counting, tapping, repeating certain words
- Ordering or arranging things for no specific reason
- Accumulating “junk” such as old magazines or empty food containers
Types of OCD

OCD Test
During the self-assessment phase, there are numerous different types of OCD tests and online quizzes available to help determine if there is a need for you to pursue the diagnosis and treatment of OCD with a mental health professional. The OCD test used can be shared with your physician to further your diagnosis and treatment. Mentioned below are some beneficial OCD test available:
- Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA) – one of the most highly regarded OCD test
- OCD Center of Los Angeles – offers a comprehensive OCD test to help determine the type of OCD you may be suffering from
- PsychCentral – is a psychology information resource that offers an OCD screening quiz
Treatment for OCD
There are some effective treatments for OCD that can help decrease the impact it has on your life.

Cognitive Behaviour Therapy and Medication
Initial treatments are considered to be Cognitive Behaviour Therapy and/or medications. Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP) is a type of CBT that has shown to effectively treat OCD. This enables you to face your obsessive thoughts and fears without putting them through compulsions.
Both licensed mental health and a medical professional will work together to develop a treatment plan involving visits to the therapist’s office a few times a week for ERP and prescribing the right medication which can alter the chemical imbalance in your brain.
Anxiety Management Techniques
Anxiety management techniques can assist an individual to effectively manage their own symptoms. These techniques can include inducing the relaxation response in the body through meditation, breathing exercises, and mindfulness. The regular practice of these techniques together with the cognitive behavior therapy treatment is the most effective.
Support Groups and Education
OCD support group allows OCD sufferers to meet in an environment that they feel comfortable and safe in and offer and obtain support. These groups help provide the perfect opportunity to learn more about the disorder and advance the social network.
Self-help tips for people living with OCD
In addition to therapy, listed below are some suggestions on how you can help yourself:
- Note down your obsessive thoughts or worries which can identify how repetitive the obsessions are.
- Make time for your worry.
- Taking care of yourself by practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation, breathing exercises, and yoga every day.
- Refocus your attention (like doing art and crafts or playing a video game). This will delay your urge to carry out a compulsive behavior.
Conclusion
To conclude, Obsessive Compulsive Disorder can have a profound effect on an individual’s life and often they are embarrassed about their symptoms and try to hide them. Therefore the disorder needs to be identified by yourself by a friend or family member before you or everyone else becomes deeply involved in the rituals causing distress and disruption. Gaining knowledge from the pointers provided above on the OCD definition, various types of OCD, its causes, symptoms, and examples of OCD, OCD test available, and OCD treatment can be highly beneficial to identify the disorder and tackle it.